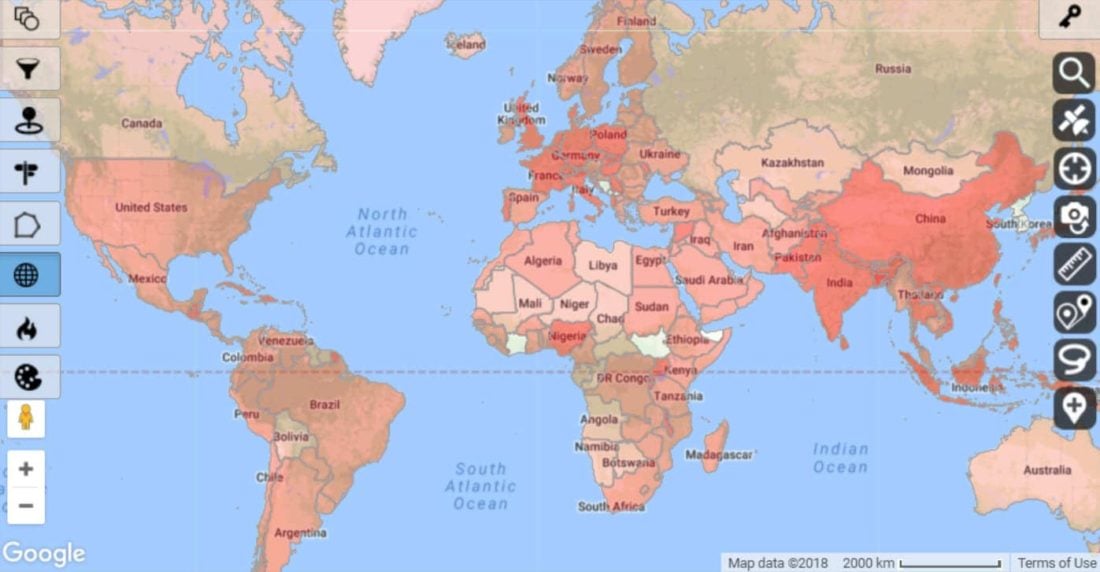
When it comes to visual representation of information, maps are an invaluable tool. They provide a way to distill complex information into a format that is not only easy to understand but also visually appealing. The map shown in this image? a. a thematic map b. a special purpose map c. a, invites us to explore the intricacies of cartography and its various forms. Understanding these maps can significantly enhance our ability to interpret geographical data and its implications on our daily lives.
Maps serve various functions; they can depict physical landscapes, demographic trends, or specific themes that resonate with particular audiences. In this article, we will delve into the different types of maps, focusing on thematic and special purpose maps. By the end of our exploration, you will have a clearer understanding of what the map shown in this image represents and how it can be applied in real-world scenarios.
As we navigate through the world of maps, it is essential to ask the right questions. What makes a map thematic? How does a special purpose map differ from conventional maps? These questions will guide us in this enlightening journey of geographical discovery.
What is a Thematic Map?
Thematic maps are designed to focus on a specific theme or subject area, providing detailed information about that particular aspect. Unlike general-purpose maps, which present a wide array of information, thematic maps isolate and emphasize a singular topic. This makes them incredibly useful for analyzing data trends and patterns.
Characteristics of Thematic Maps
- Focus on a specific theme, such as population density, climate, or economic activity.
- Utilize various colors, symbols, and scales to represent information clearly.
- Often include graphs or charts to enhance understanding of the data.
- Useful for academic research, urban planning, and policy-making.
Examples of Thematic Maps
Some common examples of thematic maps include:
What is a Special Purpose Map?
Special purpose maps are tailored to serve specific needs or goals. They are designed to present information that is relevant to a particular audience or function. These maps can include everything from tourist maps to geological maps, and they often prioritize clarity and usability for a targeted group.
Characteristics of Special Purpose Maps
- Designed for a specific audience or function.
- May not contain general geographical information.
- Utilizes unique symbols and representations tailored for the map's purpose.
- Can incorporate data such as routes, locations, and landmarks.
Examples of Special Purpose Maps
Some examples of special purpose maps include:
How to Identify the Map Shown in This Image?
To determine whether the map shown in this image is a thematic map or a special purpose map, we must analyze its attributes. Pay attention to the purpose of the map, the information it conveys, and the target audience. Understanding these factors can help in classifying the map appropriately.
What Are the Key Indicators?
- Look for thematic elements such as color coding or symbols that represent specific data.
- Assess if the map serves a particular function, such as navigation or analysis.
- Evaluate the accompanying legend or key to understand the map's purpose.
Is There Overlap Between Thematic and Special Purpose Maps?
Yes, there can be overlap between thematic and special purpose maps. For example, a thematic map showing climate patterns could also serve as a special purpose map for researchers studying environmental changes. Understanding the context and intended use of the map is crucial for proper classification.
How Can We Utilize Thematic and Special Purpose Maps?
Both thematic and special purpose maps offer valuable insights and are utilized across various fields. They can assist in decision-making, planning, and analysis. Here are some ways to leverage these maps:
- Urban planning: Assess population density and resource allocation.
- Educational purposes: Visualize data for teaching complex subjects.
- Environmental studies: Analyze climate and ecological data.
- Tourism: Guide visitors to attractions and amenities.
What Are the Limitations of Thematic and Special Purpose Maps?
While thematic and special purpose maps are incredibly beneficial, they also have limitations. Here are some considerations:
- May oversimplify complex data.
- Can be misleading if not properly designed or interpreted.
- Limited to specific themes or purposes, which may not represent the whole picture.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Maps
In conclusion, understanding the different types of maps, including the map shown in this image? a. a thematic map b. a special purpose map c. a, allows us to make informed decisions based on geographical data. As we navigate through information, maps help us to visualize and comprehend complex relationships in our world. By being aware of the characteristics, uses, and limitations of these maps, we empower ourselves to engage more effectively with the information presented to us.

ncG1vNJzZmixn6PAtr7IZqWeq6RjsLC5jq2pnqaUnruogY6mmKllmah6tLTOsKVmoZ5iwam10magppmXmnqiecBmq6GdnZbBqq%2BMppipZZJirm6%2Fz56aopmcYr22vs%2Boqp5lnZa9bq%2BMmmWhrJ2h